You don’t want to wait until spring to spring into action. The current market conditions make this winter an ideal time to move. Here’s why.
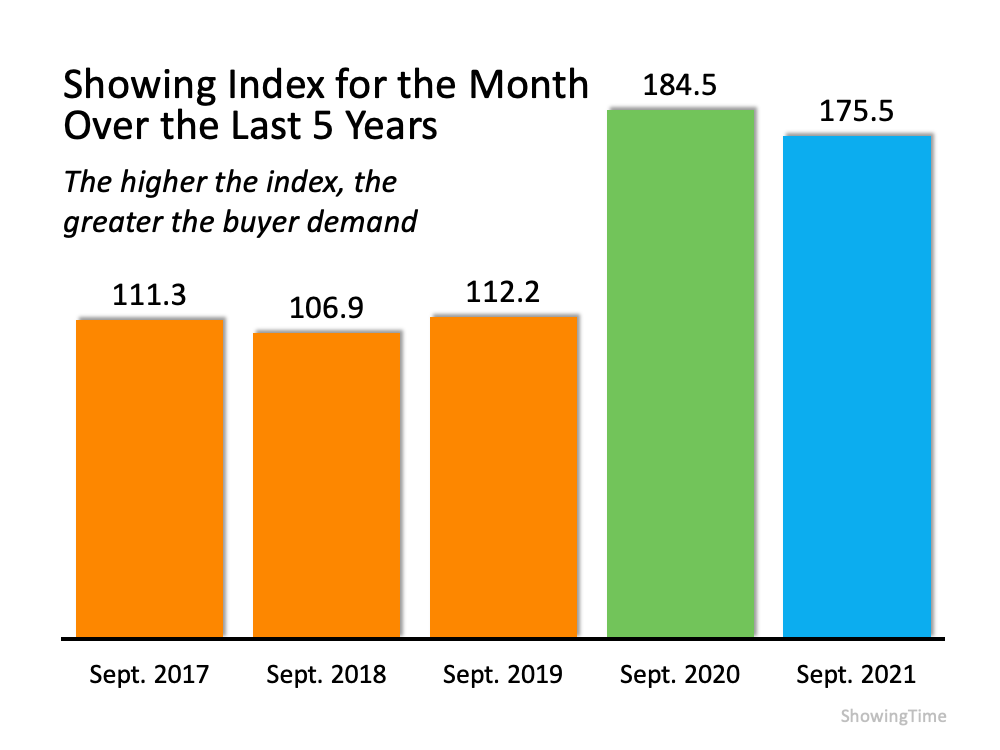
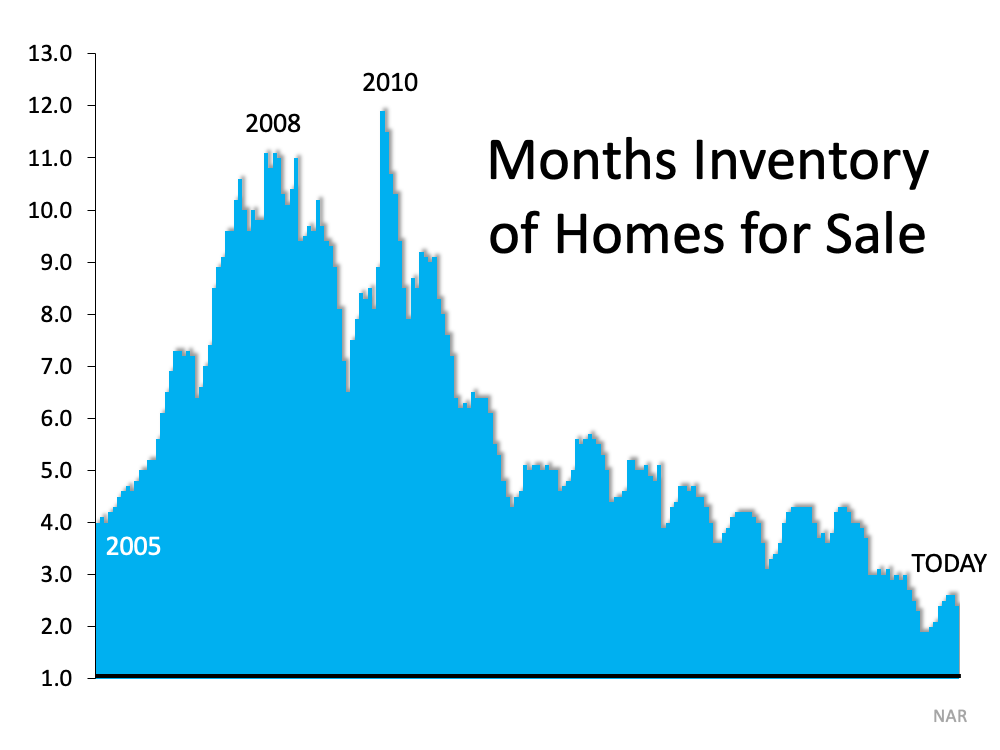
1. The Number of Homes on the Market Is Still Low
Today’s limited supply of houses for sale is putting sellers in the driver’s seat. There are far more buyers in the market than there are homes available, and that means buyers are eagerly waiting for your house. Listing your house now makes it the center of attention. As a seller, that means when it’s priced correctly, you can expect it to sell quickly and get multiple strong offers this season. Just remember, experts project more inventory will come to market as we move through the winter months. The realtor.com 2022 forecast says this:
“After years of declining, the inventory of homes for sale is finally expected to rebound from all-time lows.”
Selling now may help you maximize the return on your investment before your house has to face more competition from other sellers.
2. Your Equity Is Growing in Record Amounts
Current homeowners are sitting on record amounts of equity thanks to today’s home price appreciation. According to the latest report from CoreLogic, the average homeowner gained $56,700 in equity over the past 12 months.
That much equity can open doors for you to make a move. If you’ve been holding off on selling because you’re worried about how rising prices will impact your own home search, rest assured your equity can help fuel your next move. It may be just what you need to cover a large portion – if not all – of the down payment on your next purchase.
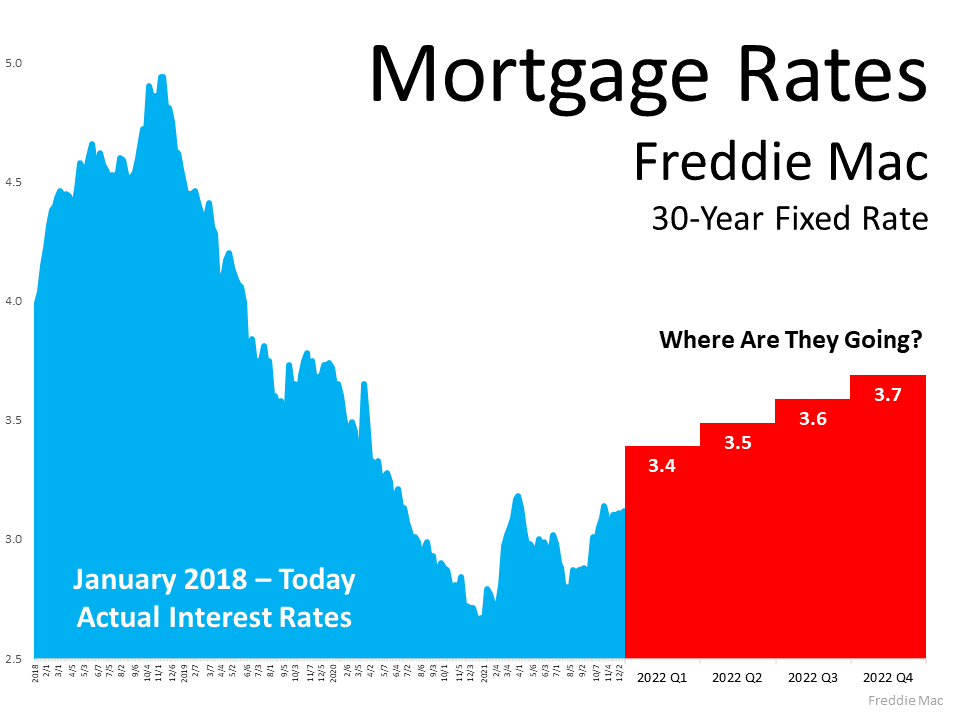
3. While Rising, Mortgage Rates Are Still Historically Low
In January of last year, mortgage rates hit the lowest point ever recorded. Today, rates are starting to rise, but that doesn’t mean you’ve missed out on locking in a low rate. Current mortgage rates are still far below what they’ve been in recent decades:
- In the 2000s, the average mortgage rate was 6.27%
- In the 1990s, the average rate was 8.12%
Even with mortgage rates rising above 3%, they’re still worth taking advantage of. You just want to do so sooner rather than later. Experts are projecting rates will continue to rise throughout this year, and when they do, it’ll cost you more to purchase your next home.
4. Home Prices Are Going To Keep Rising with Time
According to industry leaders, home prices will also continue appreciating this year. While experts are forecasting more moderate home price growth than last year, it’s important to note prices will still be moving in an upward direction throughout 2022.
What does that mean for you? If you’re selling so you can move into a bigger home or downsize to the home of your dreams, you want to consider moving now before rates and prices rise further. If you’re ready, you have an opportunity to get ahead of the curve by purchasing your next home before rates and prices climb higher.
Bottom Line
If you’re considering selling to move up or downsize, this may be your moment, especially with today’s low mortgage rates and limited inventory. Let’s connect today to get set up for homebuying success this year.

 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link



![A Happy Tail: Pets and the Homebuying Process [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2021/12/08135318/20211210-MEM-1046x1910.png)


![A Checklist for Selling Your House This Winter [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2021/12/01091834/20211203-MEM-1046x1572.png)